| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- Volatile
- 일급 컬렉션
- Spring
- synchronized
- lombok
- Dependency Injection
- OAuth 2.0
- java
- factory
- builder
- 일급 객체
- Google OAuth
- spring security
- Today
- Total
HJW's IT Blog
OS: File System 본문
1 File => 하나의 inode(index node) 를 가르킨다
inode list
1 open file table, 1 active inode table, many per-process file table
#File System Issues
> Important to user:
>> Persistence: 데이터는 전원이 꺼지거나 시스템 충돌이 발생해도 유지된다
>> Easy to Use: 쉽게 찾고, 읽고, 변경이 가능하다
>> Efficiency: 디스크 공간을 효율적으로 사용
>> Speed: 데이터에 빠르게 접근 가능
>> Protection: 다른 사람이 데이터를 손상시키지 못하게 보호
> OS 는 다음 기능을 제공한다
>> Directory and Naming: 위치가 아닌 디렉토리 및 이름으로 파일을 참조할 수 있다
>> Disk Management: 파일이 디스크의 어디에 저장되어 있는지 기록하여 빠른 접근
>> Protection: 허가받지 않은 접근 불가
# User Interface to the File System
> 파일은 저장의 논리적 단위
>> series of records
>> series of bytes
>> resource fork, data fork
# File Operations
> Create (name)
>> File descriptor를 디스크에 생성
>> 디렉토리에 이름과 file descriptor를 연결하는 entry 생성
>> 파일에게 디스크 공간을 할당
- 디스크 위치를 file descriptor 에 저장
> fileld = Open (name, mode)
>> 고유 식별자인 파일 ID를 할당하고 사용자에게 반환
>> r,w,rw 를 할당
> Close(fileld)
> Delete(fileld)
>> 파일의 file descriptor를 디스크에서 삭제하고 디렉토리에서 제거
> Read (fileld, from, size, bufAddress)
>> Random Access Read
>> FileID 에서 size byte 를 읽고 position from 에서부터 bufAddress에 명시된 위치까지
> Read (fileId, size, bufAddress)
>> Sequential Access Read
>> FileID 에서 size byte 를 읽고 현재 위치, fp 에서부터 bufAddress 에 명시된 위치까지
#Directory and Naming
> User 와 OS 는 디스크에 저장된 파일에 접근할 이름이 필요하다
> OS 는 번호를 사용하고 싶어하고 User 는 문자로 된 이름을 사용하고 싶어한다
> OS 는 디렉토리로 이름과 해당 file indice 를 기록
> Simple Naming (one single directory)
>> One name space for entire space
>> Implementation: Directory contains <name, idx> pairs
> User-based naming
>> One name space for each user
- Every name in user directory must be unique but two users can use same name
> Multilevel naming
>> Tree structured name space
>> Store directories on disk like files
>> Each directory contains <name, idx> pairs
#Common File Access patterns
> Sequential access
>> Data 는 순차적으로 프로세싱된다.
> Direct / Random Access
>> 파일 내의 byte를 직접 접근가능
# Data Structures for Files
> 모든 파일은 file descriptor 로 설명된다.
> File Descriptor 내용
>> Type
>> Access Permissions (Read, Write, ...)
>> Link Count - num of directores that contain this file
>> Owner, Group
>> Size
>> Access times - when created, last accessed, last modified
>> Blocks where file is located on disk
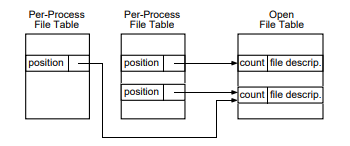

> Open File Table (하나만 존재)
>> List of all open files
>> Each entry contains
- File Descriptor
- Open count ( number of processes that have file open )
- Pointer to entry in active inode table
- Current position in file
> Per-Process File Table (many)
>> List of all open files for that process
>> Each entry contains
- Pointer to entry in open file table
- Current position in file
> Active Inode Table (하나만 존재)
>> List of active inodes
> Disk Data Structures for Files
>> File descriptor 의 내용은 디스크에도 저장되어야하며 그 성질은 persistence
>> 앞전에 다룬 내용 모두 +
>> 모든 inode가 고정크기배열 (ilist) 에 저잔된다
- ilist 의 크기는 디스크가 initialize 될때 결정
- 이 때 인덱스는 inumber 라 부른다
>> File descriptor 는
>> 처음에는 같이 저장 (inner or outer track)
>> 그 다음은 같이 middle track
>> 지금은 디스크 전체에 퍼져서 file data 에 가까운 위치
# UNIX File System
> File descriptor 는 파일을 다음과 같이 표시한다
>> 모든 inode 는 ilist에 저장
>> file descriptor 의 index 는 active inode table 에 캐시화 된다.
> UNIX 디스크는 여러 파티션으로 나누어 지는데 각각 다음 정보를 담는다
>> 디렉토리와 파일을 저장하는 block
>> Ilist 를 저장하는 block
- 파일과 알맞는 inode
- 특별한 inode
*Boot Block: code for booting system
*Super Block: 디스크 크기, number of free blocks, size of ilist, number of free inodes in ilist

# Working with Directories
> Searching a directory in UNIX
>> 파일 이름이 "/" 로 시작한다면 파일 시스템 트리의 root 에서 시작
>> 파일 이름이 "~" 로 시작한다면 user home directory 에서 시작
> Working Directories
>> A file name can be given as the full pathname separated by "/"
>> UNIX 는 각 프로세스의 현제 디렉토리의 inode 수를 기록해 둔다
>>루트 디렉토리에 저장된 정보가 하위 디렉토리의 inode 정보를 가지고 있다<<

> Directory is Table of Entries
>> 2bytes = inumber
>> 13bytes = file name
# Organization of Files (Contiguous Allocation)

> OS 는 정렬된(순서가 있는) list of free blocks 를 가진다
> 파일이 생성될 때, 인접한 블럭 그룹을 할당한다
> File Descriptor 는 시작 블럭과 파일 길이를 저장해야 한다
# Organization of Files (Linked / Chained Allocation)

> 여전히 정렬된 list of free blocks
> 하지만 file descriptor는 첫번째 블럭의 포인터를 저장
> 각 블럭은 다음 블럭으로의 포인터를 저장
# Organization of Files (Indexed Allocation)

> OS 는 list of free blockes 저장
> OS 는 파일에 의해 사용되는 모든 블럭의 포인터를 저장할 배열을 할당
> Demand 가 있을 시에만 블럭 할당
> File Descriptor는 array 를 point
# Organization of Files (Multilevel Indexed Allocation)
> 각 inode 는 13개의 block pointer 를 가진다
>> 첫 10개의 pointer 는 파일의 data blocks 를 가르킨다 (각각 512 byte)
>> 만약 파일이 10 block 보다 크다면 (5120 byte), 11번째 pointer 는 single indirect block 을 가르킨다
>> Single indirect block 은 128개 블럭을 가르키는 128개의 pointer를 가진다
>> 만약 이보다 더 크다면, 12번째 pointer 는 double indirect block
- Double indirect block: 128 개의 single indirect block 들을 가르키는 128개의 pointer
- 그 후는 triple indirect block

'OS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| OS: Paging (0) | 2023.05.23 |
|---|---|
| OS: Segmentation (0) | 2023.05.23 |
| OS: Dynamic Relocation (0) | 2023.05.23 |
| OS: Memory Management (0) | 2023.05.16 |
| OS: Deadlock Avoidance (0) | 2023.05.16 |




