| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
- java
- Dependency Injection
- lombok
- builder
- Volatile
- 일급 객체
- nestjs
- spring security
- 일급 컬렉션
- middleware
- Spring
- OAuth 2.0
- synchronized
- factory
- Google OAuth
- Today
- Total
HJW's IT Blog
DataBase: 3주 본문
# Basic Queries in SQL
> SELECT
> SQL: 테이블이 동일한 튜플 갖는것을 허용한다
>> 제약조건으로 set 을 만들 수 있다 (ex. key constraint, DISTINCT option)

5번 부서에 속한 사람들의 salary를 알고 싶을 경우
Employee table 에서, Dno 가 5인 값의 행을골라,
Fname, Lname, Salary 출력
> SELECT < attribute list> : attribute names
> FROM < table list> : relation names
> WHERE <condition> : conditional expression (boolean) that identifies the tuples
> EXAMPLE: Retrieve the birth date and address of the emploee(s) whose name is John B.Smith
{ SELECT Bdate, Address
FROM EMPLOYEE
WHERE Fname = 'John' AND Minit = 'B' AND Lname = 'Smith';
}
> EXAMPLE_2: Retrieve the name and salary of all emploees who work for the department number 5
{ SELECT Fname, Lname, Salary
FROM EMPLOYEE
WHERE Dno = 5;
}
> EXAMPLE_3: Retrieve the last name and salary of the employee(s) whose sex is male or salary is greater than 35000
{ SELECT: Lname, Salary
FROM EMPLOYEE
WHERE Sex = 'M' AND Salary > 35000;
}
> EXAMPLE_4: Retrieve the name and address of all employees who work for the 'Research' department
{ SELECT Fname, Lname, Address
FROM EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT
WHERE Dname = 'Research' AND DEPARTMENT.Dnumber=EMPLOYEE.Dno;
}
> EXAMPLE_5: For every project located in 'Stafford' list the project number, the controlling department number and the department manager's last name, address and birth date.
{ SELECT Pnumber, Dnum, Lname, Address, Bdate
FROM EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT, PROJECT
WHERE Dnum = Dno AND Mgr_ssn = SSN AND Plocation='Stafford';
}
> EXAMPLE_6: For each employee, retrieve the employee's first and last name and the first and last name of his or her immediate supervisor
{ SELECT E.Fname, E.Lname, S.Fname, S.Lname
FROM EMPLOYEE AS E, EMPLOYEE AS S
WHERE E.Super_ssn = S.ssn;
}
> EXAMPLE_7: Select all EMPLOYEE Ssns and all combinations of EMPLOYEE Ssn and DEPARTMENT Dname in the database
{ SELECT Ssn
FROM EMPLOYEE;
}
{ SELECT Ssn, Dname
FROM EMPLOYEE , DEPARTMENT;
}
> USE of *
>>
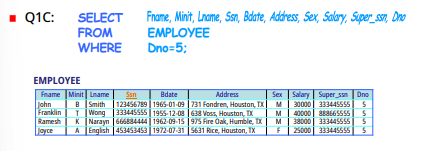
SELECT *
FROM EMPLOYEE
WHERE Dno=5;
# Table as Sets in SQL
> 왜 SQL 은 동일한 여러개의 튜플을 허용하는가? -> Duplicate Elimination 은 비싼 작업이다
> User 가 필요에 의해 여러 튜플을 넣어놓았을 수도 있다
> EXAMPLE_8: Retrieve the salary of every employee
{ SELECT ALL Salary
FROM EMPLOYEE;
> EXAMPLE 9: Distict salary values
{ SELECT DISTICT Salary
FROM EMPLOYEE;
> EXAMPLE_10: Make a list of all project numbers for projects that involve an employee whose last name is 'Wong' either as a worker or as a manager of the department that controls the project
{ SELECT DISTINCT Pno
FROM WORKS_ON, EMPLOYEE
WHERE Essn = Ssn AND Lname='Wong'}
UNION
{ SELECT DISTINCT Pnumber
FROM PROJECT, DEPARTMENT, EMPLOYEE
WHERE Dnum = Dnumber And Mgr_ssn = Ssn And Lname = 'Wong'}
> EXAMPLE_11: Retrieve the names of all employees whose address is in Houston, Texas
{ SELECT Fname, Lname
FROM EMPLOYEE
WHERE Address LIKE '%Huston, Texas%'}
> EXAMPLE_12: Find all Employees who were born during the 1950s
{ SELECT Fname, Lname
FROM EMPLOYEE
Where Bdate LIKE '__5_______'}
> EXAMPLE_13: Show the resulting salaries if every employee working on the 'ProductX' project is given a 10% raise
{ SELECT Fname, Lname, 1.1*Salary AS INCREASED_SAL
FROM EMPLOYEE, WORKS_ON, PROJECT
WHERE Ssn = Essn AND Pno = Pnumber And Pname = 'ProductX'}

> EXAMPLE_14: Retrieve all employees in department 5 whose salary is between 30000 40000
{ SELECT *
FROM EMPLOYEE
WHERE Salary BETWEEN 30000 AND 40000 AND Dno=5;
}
# Ordering of Query Results
> EXAMPLE_15: Retrieve the first and last names and Dno of all employees, ordered by department number and within each department, ordered alphabetically by last name, first name
{ SELECT Fname, Lname, Dno
FROM EMPLOYEE
ORDER BY Dno, Lname, Fname;
}
> EXAMPLE_16: Retrieve a list of employees and the projects they are working on, ordered by department and within each department, ordered alphabetically by last name, first name.
{ SELECT Dname, Lname, Fname, Pname
FROM DEPARTMENT, EMPLOYEE, WORKS_ON, PROJECT
WHERE Dnumber = Dno AND Ssn = Essn AND Pno = Pnumber
ORDER BY Dname, Lname, Fname;
}
# Insert Command
> INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE
VALUES ('Richard, 'K', 'Marini', '653298653', '1962-12-30', '98 Oak Forest, Katy, TX', 'M', 37000, '987654321', 4)
> INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (Fname, Lname, Dno, Ssn)
Values ('Richard', 'Marini', 4, '653298653');
>> 다른 명시되지 않은 값들은 DEFAULT 또는 NULL 로 처리
>> , 를 사용해 여러 튜플 삽입도 가능

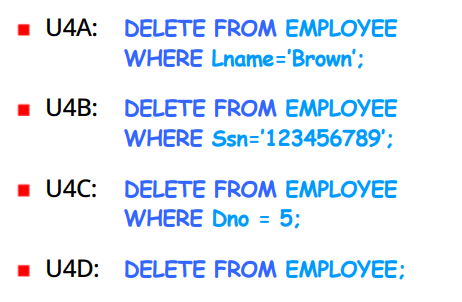
#DELETE Command
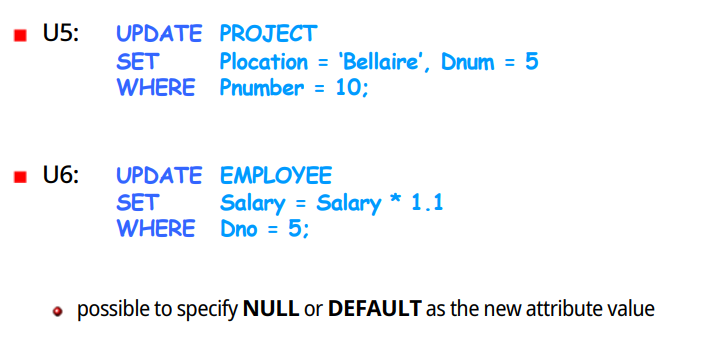
#UPDATE Command
'Database' 카테고리의 다른 글
| PostgreSQL 격리 수준 제대로 이해하기: MVCC·VACUUM·SSI (3) | 2025.08.24 |
|---|---|
| [Database Studio] 2주 수업 정리 (0) | 2024.05.26 |
| Complex Query 2 (0) | 2023.09.22 |
| DB: Chapter 7(Complex Queries) (0) | 2023.09.16 |
| Database: 1주차 (0) | 2023.08.29 |


